For many control systems in real life,
impulses and delays are intrinsic phenomena that do not modify their
controllability. So we conjecture that under certain conditions the abrupt
changes and delays as perturbations of a system do not destroy its
controllability. There are many practical examples of impulsive control systems
with delays, such as a chemical reactor system, a financial system with two
state variables, the amount of money in a market and the savings rate of a
central bank, and the growth of a population diffusing throughout its habitat
modeled by a reaction-diffusion equation. In this paper we apply the Rothe’s
Fixed Point Theorem to prove the interior approximate controllability of the
following Benjamin Bona-Mohany(BBM) type equation with impulses and delay
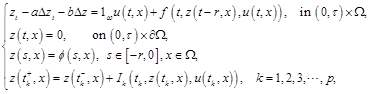
where
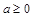
and
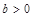
are constants,
Ω is a domain in
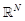
,
ω is an open non-empty subset of
Ω ,
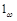
denotes
the characteristic function of the set
ω , the distributed control
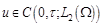
,
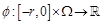
are
continuous functions and the nonlinear functions
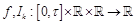
are smooth enough functions
satisfying some additional conditions.