A quantum statistical theory of the superconductivity in MgB
2 is developed regarding it as a member of the graphite intercalation compound. The superconducting temperature
Tc for MgB
2, C
8K ≡ KC
8, CaC
6, are 39 K, 0.6 K, 11.5 K, respectively. The differences arise from the lattice structures. In the plane perpendicular to the c-axis, B’s form a honeycomb lattice with the nearest neighbour distance
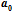
while Mg’s form a base-hexagonal lattice with the nearest neighbour distance
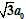
above and below the B-plane distanced by
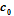
. The more compact B-plane becomes superconducting due to the electron-phonon attraction. Starting with the generalized Bardeen- Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) Hamiltonian and solving the generalized Cooper equation, we obtain a linear dispersion relation
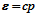
for moving Cooper pairs. The superconducting temperature
Tc identified as the Bose-Einstein condensation temperature of the Cooper pairs in two dimensions is given by

, where
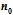
is the Cooper pair density,
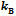
the Boltzmann constant. The lattices of KC
8 and CaC
6 are clearly specified.