There is growing evidence to suggest that the black hole mass has been previously underestimated with the H
b line width for certain Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN). With the assumption of the flatter rather than isotropic velocity distribution of gases in the broad-line region of AGN, we investigated the properties of Narrow Line Seyfert 1 (NLS1) galaxies, like the black hole mass and the Eddington ratio, and compared with Broad Line Seyfert 1 (BLS1) galaxies. Since gamma-rays detected in a few NLS1s which favored a smaller viewing angle in NLS1s than BLS1s, with the projection effect, we estimated the relative black hole mass and Eddington ratio for NLS1s and BLS1s. The result implies that the NLS1s and BLS1s have similar black hole masses and Eddington ratios, peaked at a larger black hole mass and lower Eddington ratio for the NLS1s than thought before. Furthermore, with applying the correction factor 6 of average black hole mass as derived from the modeling of both optical and UV data in radio-loud NLS1s by Calderone et al., to the Xu et al. sample, we find that the NLS1s and BLS1s also show similar black hole masses and Eddington ratios, peaked at 2.0 × 107 solar masses and 0.12 (Eddington ratio) for the NLS1s. The
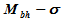
relation due to the enhanced black hole masses of NLS1s is discussed. In addition, there seems to show a linear correlation between jet power and disk luminosity for the flat spectrum radio-loud NLS1 sample, which implies an accretion dominated rather than black hole spin dominated jet.