Application of Five-in-One Community Management Mode plus Wuhan’s Regional WeChat Platform in the Novel Coronavirus Control ()
1. Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak was a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) [1] [2] [3] on January 30, 2020. Chinese society pays close attention to the method and effect of community-based control of the novel coronavirus outbreak. Wuhan government has built the five-in-one community management structure and created the WeChat platform account named “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” for on-line and off-line grid management of the community residents. Through this WeChat platform, scientific and standardized health propaganda is carried out, and the residents are instructed on self-care and home quarantine. A good effect has been achieved with this combined approach in curbing the spread of novel coronavirus. In this study, a brief introduction is provided for this novel coronavirus control mechanism.
2. Background
December 2019 marked the beginning of the 2019-nCoV outbreak in Wuhan, when the local community residents still lacked a basic understanding of the infectivity of this disease. One patient with fever might visit the outpatient clinic of several ordinary hospitals either in their cars or by taking public transportation in a “shopping-like manner,” which was also hazardous to public health. There was no effective defense barrier raised between the medical institutions already put under great risk and the general mass lacking in defense capacities. A large number of patients infected by novel coronavirus, close contacts, and coronavirus-carrying patients in the incubation period traveled between the communities and hospitals without any restrictions, which further facilitated the pathogen spread. The mortality among the elderly patients and those with chronic underlying diseases was once very high, causing social panic and unrest, which in turn added to the difficulty of novel coronavirus control.
The State Council held a series of press conferences in Beijing on the joint prevention and control of the novel coronavirus, requiring the implementation of the anti-output, anti-input and anti-spread measures against the epidemic. The novel coronavirus outbreak in China began in tandem with the Lunar New Year when the population mobility was high, people gathered together for the festival and the peak time for passenger transport occurred. The local communities have limited capacities in providing treatment for the patients, though fortunately, the spread of the epidemic can be more easily controlled on the community level. Based on the anti-SARS experience back in 2003, experts are leading the guidance of the development of a variety of countermeasures in Wuhan. The five-in-one community management mode plus Wuhan’s regional WeChat platform comes into being, which is considered an innovative approach for grid management of the community residents. Thus, an integrated scheme of on-line and off-line community-based novel coronavirus control is carried out. All forces of the society and mobilized and organized together in response to the novel coronavirus outbreak, with the communities acting as the basic unit in this battle.
3. The Implementation Scheme of Five-in-One Community Management Mode plus “Wuhan Neighborhood on WeChat” Consists of the Following
3.1. Five-in-One Community Management Mode Is Built to Carry out All-Around Propaganda on Anti-Coronavirus Knowledge for the Public
Communities are the front line for joint prevention and control of the epidemic and also the most effective defense against the input of the disease from the outside and spread of the disease on the inside. The five-in-one mass prevention and mass treatment group consists of grid management coordinators of the community resident committee, the cadre of women’s federation, civil police, medical workers, property cleaning personnel, and other community service personnel. They are the backbone of off-line community resident services, which compose the robust defense line of mass prevention and mass treatment, responsible for the all-around implementation of various measures of joint prevention and control. The electronic displays in residential buildings, property bulletin boards, community loudspeakers, and popular science bulletin boards along the streets, which are widely found in the communities but involve no interpersonal contact, are fully utilized for the promulgation of Letter to the Residents. These are important media to spread the knowledge on novel coronavirus control as well as the contact information of the community management coordinators and cadre of women’s federation. By these means, the community residents can be fully informed of the procedures of seeking medical services [4] [5]. The information of the residents is collected with the building as the unit so as to facilitate novel coronavirus control and management. The ultimate purpose is to cover every resident in the community, let every resident know of the relevant information and knowledge on novel coronavirus control, and ensure their full operation.
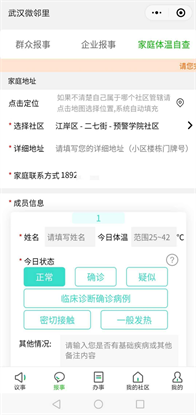
3.2. Residents Are Required to Do Real-Name Registration at “Wuhan Neighborhood on WeChat”, So That They Can Receive Fever Monitoring
“Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” is a mini-App developed under the supervision of the Wuhan government, which localizes the family address of every resident by satellite positioning, as well as the community resident committee to which the residents are subordinate and the volunteers providing service to these residents. Thus an on-line grid structure and virtual cloud are built to connect the residents, community resident committees, and community volunteers. “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” plays an unexpectedly vital role in the battle against novel coronavirus. The mass prevention and mass treatment group performs household-to-household screening for all residents who have done real-name registration at “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” from 1159 communities in the central urban area in 15 districts of Wuhan. The screening is realized by telephone calls, WeChat and door-to-door visits. The government policies, epidemic prevention information, and activities of the community resident committees are sent via the WeChat platform to reach the residents at any time necessary. At 10 am, 2 pm and 4 pm every day, the community management coordinators will inquire about the residents’ health status via WeChat, guiding self-monitoring of body temperature. Residents with fever are recorded and registered on a full scale with timely reporting to the regional headquarter for prevention and control of novel coronavirus. The customer service of “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” is 24 hours on duty. Network diagnosis is triggered upon receiving any alert signals. The patients will be guided on home quarantine, and the address is located and registered by satellite positioning, so as to track the disease progress and to know of the patients’ status (hospitalization or home quarantine). In the meantime, other populations will be warned to stay away from the places of isolation. In this way, the isolation measures of “early discovery, early reporting, early treatment, and centralized treatment” are carried out to the smallest detail.
3.3. Community-Level Medical Institutions Are Responsible for Primary Screening and Triage Process
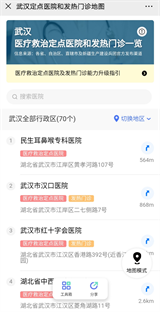
Given the fast speed of epidemic spread, the designated hospitals in Wuhan have reallocated the beds and set up the isolation units. Therefore, ordinary hospital beds decrease dramatically, resulting in an unprecedented shortage of medical resources, and there are hardly any hospital beds left for other diseases. The triage process is started in response to the isolation requirements of novel coronavirus infection, to relieve the workload and shorten the waiting time at the fever outpatient clinics at large hospitals, and to reduce cross-infections. The grassroots medical institutions are responsible for handling first visits, screening, and classification of the patients with fever and supervising home quarantine of suspected cases or patients under medical observation. “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” mini-App timely pushes the address and contact information of 70 fever outpatient clinics in the whole city and that of the isolation centers in each district to the residents; it also releases information on community-level designated medical institutions, to guide the confirmed or highly suspected patients to seek medical care at these institutions [2].
3.4. Mass Prevention and Mass Treatment Is Adopted, with the Implementation of Infectious Disease Reporting System on the Community Level
National Health Commission of PRC considers classified novel coronavirus infection as a class B infectious disease in the Law for the Control of Infectious Diseases of PRC but adopts the preventive and control measures generally used for class A infectious diseases. Novel coronavirus infection has also been put under quarantine supervision of infectious diseases according to the Frontier Health and Quarantine Law of PRC. Infectious disease reporting is a highly professional working system. Wuhan has created and implemented the daily reporting system for novel coronavirus control work via “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat.” Professional personnel in infectious diseases at hospitals guide the five-in-one mass prevention and mass treatment group and relevant staff on daily reporting of the novel coronavirus control work, with the goal of fast, transparent, and complete release of the epidemic-related information.
3.5. Suspected and Mild Patients Are Admitted to Designated Facilities to Promote the Community Safety Level
In order to protect other community residents from the places of isolation, the Wuhan government has expropriated private hospitals, hotels, party schools, and other schools for concentrated isolation. These sites for the isolation of suspected cases and close contacts. Eleven public sports facilities are expropriated and converted to module hospitals [6], which receive mild cases. These measures have effectively relieved the shortage of medical resources in Wuhan and also lifted the psychological burden from the local community residents who worry about being infected. Family doctors are assigned to home quarantine of mild patients without severe underlying diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems [4], with the implementation of “four once”: distributing disinfectants and guiding home disinfection once, inquiring about the disease course on the telephone once daily, providing health consultation for home quarantine once, and sending special vehicles to take the highly suspected cases to the designated hospitals once. In the meantime, life services are provided for those during the quarantine. Volunteers deliver vegetables, medicine, and meals to those during home quarantine to satisfy the basic life needs of people in concentrated isolation sites or in isolation.
3.6. The On-Line Hospital Registration and Appointment System Is Implemented for Patients with Fever So That the Patients Can Visit the Doctors in an Ordered Manner with Less Waiting Time and Less Population Aggregation
The five-in-one mass prevention and mass treatment group provides on-line and off-line grid services via the “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat”, including making an appointment at the designated hospitals for patients with fever and arranging special vehicles to take them to the hospitals. Office visits at a different time greatly reduce the waiting time for patients at the hospitals [7]. This measure ensures that the patients can be received as soon as possible and avoids the infection risk for patients or their relatives who otherwise need to wait up in long queues at hospitals or travel between different hospitals.
3.7. Special Vehicles Are Allocated for the Transferral of Patients with Fever, and the Terminal Disinfection Measures Are Strengthened for Vehicles and the Public Places Exposed to These Patients
Wuhan also recruits about 6000 cruising and online-booked taxis as emergency vehicles, which are allocated to 1159 communities in the central urban area and subject to centralized dispatch by the community resident committees. These vehicles are reserved for taking the suspected or confirmed cases of novel coronavirus infection to designed hospitals. It is required that the drivers, patients and the accompanying patients riding the taxis must wear surgical masks and perform hand hygiene. Guidance is provided for the terminal disinfection of the places exposed to transferral vehicles and patients. Disinfection includes spraying the places with 2000 mg/L chlorine-containing disinfectant and closing the places for 60 min after the spraying. After the disinfection, all objects are wiped with clear water to ensure the elimination of the pathogens from the vehicles, places, and various objects [8] [9].
3.8. Daily Caring Plan Is Implemented, and Psychological Support Is Provided for Patients and Special Populations
To safeguard the psychological health of the community residents and to encourage the public’s participation in novel coronavirus control, the five-in-one mass prevention and mass treatment group also offers psychological consultation via “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat” to relieve the stress arising from the epidemic. A call for members of the Communist Party and social volunteers is sent out to encourage participation in the grid group created by “Wuhan neighborhood on WeChat”. Their responsibilities include reporting the monitoring of special populations in areas under administration, caring for the elderly, left-behind children and seriously ill neighbors, and weaving an all-around health caring network. The purpose is to make ensure that every person, every hour and every incident are being attended to and to avoid the spread of epidemic due to the lack of caring for those in isolation.
4. Result
Wuhan is currently challenged by the deficiency of health resources and the limited service capacities of professional medical staff. Ever since the implementation of five-in-one community management mode plus Wuhan’s regional WeChat platform, all available social material and human resources are mobilized, including the Party and the League backbones, community volunteers and even the general public. This novel coronavirus control mode has consolidated the basis of self-governance and self-protection of the communities. A wide array of measures have been adopted for novel coronavirus control, including public health propaganda, administration and tracking of migrant populations, self-quarantine of close contacts, standardized rectification of community environment, and carpet-like tracking of suspected cases at the peak of the epidemic outbreak, and grid management. Every household and every person in the community can be accessed through this control mode, which improves the efficiency of community-based novel coronavirus control. By February 29, Wuhan had 48 designated hospitals that accepted patients infected by novel coronavirus. Plus the newly added bed in other hospitals, there were a total of 26,911 beds for patients infected by novel coronavirus. Sixteen module hospitals that accepted mild patients had over 20,000 beds, and the centralized isolation spots had 11,172 beds. These medical resources can greatly relieve the shortage of hospital beds for the infected patients in Wuhan, thereby meeting the goals of “admitting every patient that needs to be admitted”. More patients can receive timely treatment at these medical institutions, with separated and centralized admission of four types of patients, namely, mild, ordinary, severe, and critically ill, which represents an effective implementation of the triage process and differentiation of infectious disease management based on the type and severity of patients. Mild patients and populations under medical observation are also properly handled, which helps boost social stability.
5. Discussion
Safeguarding social stability is one of the top proprieties in the face of a major epidemic outbreak. Communities are the front line of joint prevention and control of the novel coronavirus and also the most effective defense against the input of the epidemic from the outside and spread of the epidemic on the inside. The communities should fulfill the principal role in joint prevention and control of the epidemic outbreak, extensively mobilizing and relying on the mass to make communities the robust fortress against the epidemic outbreak. The five-in-one community management mode plus Wuhan’s regional WeChat platform in the novel coronavirus control proves to be an effective approach to health education and public opinion guiding. This integrated strategy coordinates the on-line and off-line novel coronavirus control efforts, consolidating confidence, bringing warmth and cohesion to the general public, and maintaining social stability. Five-in-one community management mode plus Wuhan’s regional WeChat platform offers new community-level experience and inspiration for novel coronavirus control and contributes to the overall people’s war on the virus. It represents concrete steps taken to protect people’s life safety and physical health.
NOTES
*Both authors contributed equally to this paper.