
1. Introduction
With the improvement of people’s level of knowledge, the library has become an indispensable part of daily life. But the library storage and the business volume are huge, the traditional accounts’ management is merely not feasible. At the time, library management system comes into being and becomes an important part of information construction gradually. In order to develop, build and adapt to the modern information society, establishing a management information system becomes the main trend, and also we can’t avoid the problem. The implementation of electronic book management can help human resource officials free themselves from the heavy deskwork to complete some more important work. Library management system is to reduce and solve the cumbersome manual management, so that the library can rise to a perfect electronic management.
The history of the library management system could date back to the late 1960s. At that time, computer technology had entered the practical stage. Meanwhile in most large-scale libraries, it’s very time-consuming and easy to make mistakes to find books or statistical information manually. In order to solve this situation, the first generation of book lending management system came into being. But due to the immature technical conditions and the constraints of demands, the user was very small. There was no doubt that its appearance showed a bright future for the management of book lending, that is, with the computer’s high speed and automation to replace the huge amount of manual work and with the computer’s high accuracy to avoid manual mistakes and errors. The second generation of the library management system appeared in the late 1970s. On account of the rapid development of computer technology, whether the popularity of computers, or the developments of computer system tools and database technology, it provided the possibility for the phasic development of library lending management system. But it failed to systematically consider the needs and concepts of book borrowing.
The revolutionary change in the library management system occurred in the late 1990s. With the information explosion and the arrival of the era of knowledge-driven economy, individuals, units and social had a higher demand on library management system. In the meantime, due to the pullulation of database technology, customer/server technology, especially Internet/Intranet technology, the third generation of books borrowing management system had become inevitable. The third generation of library management system was characterized by the angle of book borrowing management, it dealt with almost all data related to the book lending with a centralized database. The friendly user interface, powerful report generation tools, analysis tools and information sharing allowed managers to get rid of heavy daily work and focus on planning and policies of book lending from a strategic perspective.
At first, the library management system software is mainly written in assembly language. With the birth of C language and its advantages and powerful features (from [1] ), library management system based on the C language produced. The author [2] pointed out: at this stage, digital library management system is a prerequisite for students to create a better reading environment. The core is how to make it with the perfect combination of the Internet, and truly achieve timeliness and accuracy. Authors in [3] and [4] have analyzed the status of the digital construction of university libraries, and tried to put forward their own construction plans for the digital construction of local university libraries. The authors in [5] pointed out that many miniature libraries had begun to fully understand the importance of computer technology in library management, and began to use computer technology to achieve the practical application of library books. However, miniature libraries usually have fewer funds, lack of professional management and have other issues. There are many problems of using such a large system, so small and medium-sized libraries do not have such conditions to configure large-scale systems. In view of this problem, the development of miniature library management system has become an urgent affair. Some authors in [6] mentioned it respectively specifics the development process of the library management from the demand analysis and summary design to the detailed design system. And it minutely introduces the interaction between the various modules of library management system. Through the development of the system, it solves some contradictions in the management of library data and achieves the efficient management of data. Basing on Visual Basic 6.0 and SQL Server 2000 system developing to achieve a new library management system is imperative. The author in [7] used mainly B/S structure and ASP. NET + SQL Server technology as a web development tool to develop the public book system. Firstly, it makes a system analysis and divided the main function of the system. Then, it provides the key technology of the system design and the database design of the system. In [8] an implementation procedure of library management system database design and system function was introduced. It used C/S and B/S combined technology to achieve the book and journals computer network management and Web query function. With the increasing of volume, the difficulty of books recorder and inquiry also increased. Then usual methods cannot meet the requirements. In [9] , the author pointed out that the development of library information system mainly includes two aspects: using database technology and developing application systems. In [10] , authors elaborated some thoughts about the problems existed in the processing of library digitization. In [11] , a sub-cycle management library 2.0 model was proposed. Taking VC as the development platform, the book information management system is under the Dos system and based on C language. Its simple and friendly interface and Compact structure make it easy to operate. System objectives are: for the administrator, it provides all the details of the borrower, as well as the details of the library inventory; for students or ordinary users, it has two functions includes borrowing and returning books; the administrator can also record new books, delete old books and so on. Visitors can also enter the system without a registering user, but there are certain functional limitations.
2. Need Analysis of the System
The system is divided into three parts: administrators, student users and unregistered users (visitors).
Administrators have the following functions: 1) Password verification Login: only the administrator inputs correct account and correct password can enter the administrator interface. If you input wrong account, the system will show the account error and you can’t enter the administrator system interface. Similarly, if you enter the wrong password, the system will display password error and you also can’t enter the administrator system interface. 2) Register a new book: When the administrator successfully landed, the administrator can input the basic information of the book to add a new book to the book system. 3) Delete the old book: the administrator can input the book number (book unique identification) to delete books from the book system.
Student users have the following functions: 1) Password verification Login: only the user inputs correct account and correct password can enter the administrator interface. If you input wrong account, the system will show the account error and you can’t enter the user system interface. Similarly, if you enter the wrong password, the system will display password error and you also can’t enter the user system interface. 2) Borrow books: the user inputs the number of a book and also their correct account and password to borrow books successfully. 3) Return books: only the user inputs the number of the borrowed books and also their correct account and password to return the book successfully. If the user has not borrowed this book, the system will output “never borrowed the book.” If the account or password is wrong, the system outputs “account error” or “password error”. 4) Look up their borrowed books and personal circumstances: the user can view their basic information and what books they have borrowed.
Unregistered users (visitors) have the following function: visitors can browse all the book information, but they can’t borrow books. They can also register new users by filling out the student’s basic information.
3. Designs of the System
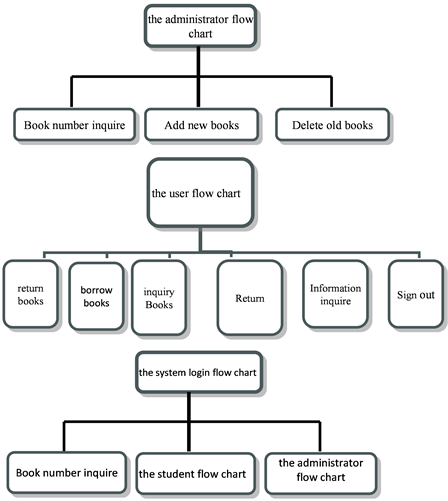
3.1. Main Flow Chart
The main flow chart consists of three parts: the system login flow chart, the user flow chart, the administrator flow chart.
3.2. Main Data Definition of System
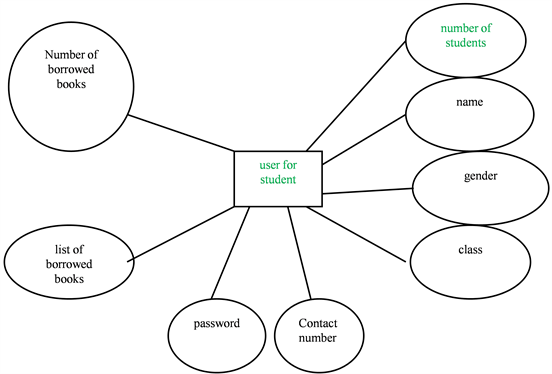
The basic definition of student entity and attribute: student user (student number, name, gender, class, list of borrowed books, number of borrowed books, contact number, password).
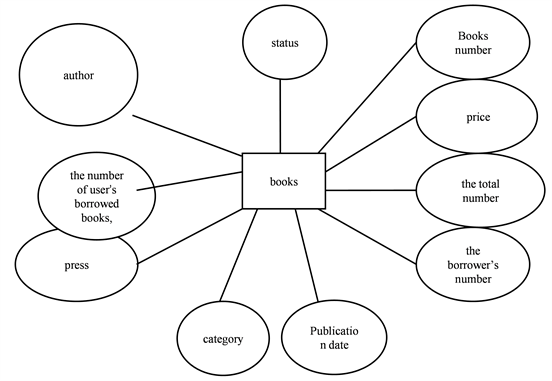
The basic definition of book entity and attribute: books (book number, book name, author, unit price, the number of user’s borrowed books, the borrower’s number, the total number, whether to lend).
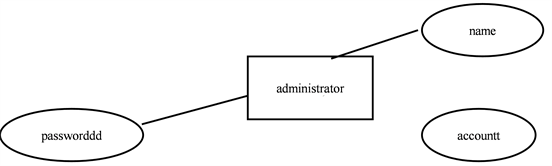
Basic definitions of administrator entities and attributes: Administrator (account number, name, password).
3.3. Design Thoughts of Core Performance Function
Login Module: void main loging (); void youke_loging (); void student_loging (); void aimid_loging (); void SPassword (); void APassword ();
Page Module: void zhuyemian 1 (); void aimid_yemian (int c); void Yonghu_yemian (int c); void visiter_yemian ();
Administrator Module: void Bookview (int c); void Addbook (int c); void Deletebook (int c); int Findbook (int c, int bn); void Delete 1 (int c); void onghuview (c);
void Yonghu_guanli (c); void Delete_Yonghu (c); void Init_mima (c);
User Module: void n_Findbook (int c); void b_Findbook (int c); void m_Findbook (int c); int mohuchaxun (char s[], char t[]); void Findbook_yemian (int c); void bookBarry_yemian (c); int Findbook 1 (int c, int bn); void bookReturn (int c);
Visitor Module: 1) New user registration function: unregistered users can register to be a user; 2) User login module (combined with administrator login and user login): only the user inputs correct account and correct password can enter the user interface. The concrete verification function is implemented by S Password (). If you enter wrong account, the system will show an account error and you cannot enter the user system interface. Similarly, if you enter wrong password, the system will display a password error and you cannot enter the user system interface.
4. Software Testing
Software testing plays an important role in the software lifecycle. In the traditional waterfall model, software testing is only in the operation and maintenance phase, and it is an important means to ensure the quality of the software before the software products are delivered to the user. Recently, the software engineering community tends to a new view that the software lifecycle should be included in each stage of the test, so as to test the results of this stage if it’s close to the expected target, as soon as possible to find errors and amendments. If not testing in the early stages, the wrong delay spread often leads to the great difficulty of the final product testing.
The system completely uses code blocks programming tools, so the demanding software runtime environment is more common and easy to operate. System testing: using manual testing methods for system testing and starting from the program debugging for the reason that software design needs to compile a lot of code. But its wrong frequency is quite high. If there is no error, then test each single module. After passing the test, then connect it with other modules to see if the overall design is reasonable. At the beginning of the test, it is not necessary to carry out the data in the real case, and some well-designed data can be used as a test case. This will not only reduce the processing workload, but also easier to find the error and determine the scope of the error. Functional testing of the test object should focus on all testing requirements which can be directly traced to use cases or business functions. Mainly using the black box test method to test some of the system modules:
User login The administrator login page is red, and the user login page is sky blue. When the login account and password have errors more than three times, it suggests whether to re-enter.
New book stock in Inputting the correct account password, entering the function modules of adding books in the administrator page, and it shows if it’s successful to add books after enter the new book information.
Delete old books In the administrator page, you should select the delete book function and enter the information of the book. If the book does not exist, it should prompt the book does not exist. When you find the book successfully and confirm the deletion, it shows delete the book successfully, and you can see whether it was deleted successfully in the query module.
User management Administrators can manage user’s information, modify user rights, log out users, and also initialize user login passwords, but administrators can not add users at will.
Borrowing books After the user login successfully, select the borrow function, enter the correct information of the book, you can achieve the function of borrowing books. And you can’t borrow books before confirmation of user information, at the same time, system modifies the book borrow information.
Returning books After the user borrows the book, you can choose to return the book. If you return the book that is not borrowed, it will suggest if you borrowed this book or return the book once again. And at the same time, system updates the book borrow information.
Library inquiry Users can select the book query function to view books. You can choose number query, bibliographic query and fuzzy query. System will display the corresponding book information. When the user chooses a fuzzy query and enters a keyword such as a part of the title, the corresponding matching book can be obtained.
User register Visitors can register the user on the visitor page. They can register as a user after entering the legal user number and user information. In the meantime, they should set their own password, and can log on the user page.
5. Conclusion
With the development of network technology, the existing library management system is more and more perfect, and the system function becomes more and more comprehensive. Its convenience and usability cannot be comparable. So this article concerns library management system based on the C programming language, compared the system with now popular library management software, it has some advantages. From the angle of system development, the system has completed some functions such as add, delete, correct, inquiry of the library management system, as well as the user independent query borrowing function. It is better to complete the system development objectives and requirements. But there are also some shortcomings. Coupled with limited personal time, the system appears some errors and hidden bugs, such as data storage capacity is limited. When the number of student users and books increase, the system cannot be used, and the changes that the system made to the data can’t be saved for a long time. Each time the system restarts, data also updates. What’s more, the system is the interface system, it has cumbersome operation. For example, each time, that users borrow books needs to pass the password for user authentication.
Acknowledgements
Supported by the Teaching Reform Foundation of Huanggang Normal University (2017CE12, 2014kg15).