An Application Expert System for Evaluating Effective Factors on Trust in B2C WebsitesTrust, Security, ANFIS, Fuzzy Logic, Rule Based Systems, Electronic Commerce ()
1. Introduction
Recent use of electronic commerce and especially the type of B2C has increased remarkable and electronic commerce is newly operating under its expected capacity, principally because merchants find it very difficult to trust one another online for trading decisions. It is therefore very important to develop an effective trust management system that aid e-commerce participants to make right decisions on electronic B2C websites. Trust is considered as a critical fact for the success of e-commerce. Online trading has introduced new problems and challenges to online buyers: The uncertainty about the quality of products or services and the ability of sellers to stay anonymous have lead to a high level of risk in online transaction environments, virtual communities and online auctions [1,2].
However, according to a survey by Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), security and then trust are still some of the main key problems in the e-commerce world, all of which directly or indirectly have significant impact on trust [3]. Trust management systems therefore can help to reduce risk (e.g., ID theft), and make it easier for users and agents to interact with one another in a low risk environment. The importance of trust management has also been increasingly acknowledged due to the advent of virtual communities. Since participants in these communities do not know each other and do not have face-to-face contact, the ability to provide a system that allows communication to be done in a trusted environment is vitally desirable [2].
Thus, it is necessary to provide guidelines for B2C companies through a study on the components of B2C Website that affect on customer trust. So the aim of the paper is studying and evaluating customers in B2C Websites, and attempts to find out the relationship among the factors of the customer trust and B2C websites. Additionally, this Study set up an evaluation system of customer Trust, in which there contains three main factors security, design and familiarity. Figure 1 shows key problems in electronic commerce.
Spending on online marketing in Europe will double in the next five years, from around 7.5 billion euros in 2006 to more than 16 billion euros in 2012, according to a new Forrester report, “European Online Marketing Tops 16 Billion In 2012.”
Online marketing—email, and search and display advertising—will account for 18% of total media budgets in Europe in five years, according to the projections.
The reason for this shift in spending is that audience and attention are moving online, according to Forrester research Inc:
• Some 52% of Europeans are regularly online while at home, and 36% of online Europeans say that they watch less TV because they’re online.
• On average, they spend three hours per week more online than watching TV.
• Consumers’ reliance on online services is growing
• 36% of online adults have recently downloaded music online, and 20% have downloaded games
• 35% have bid or sold in online auctions
• Trust in many types of advertising is eroding: 67% of online consumers say advertisers don’t tell the truth in ads.
• 34% of online consumers say they don’t mind ads if they relate to their interests.
• 40% of online consumers trust price-comparison sites.
• 36% of online consumers trust online product reviews from other users.

Figure 1. Key problems in electronic commerce [3].
The Trust model presented in this study has various aspects of consumer trust, online Environment, website designs, security and familiarity of websites. We have also addressed the importance of online customer service and its impact on consumer trust. The trust model highlights the importance of building trust in the online environment with the process of customer service. The contribution to theory of this paper is based on empirical data and information from three websites regarding our research problem.
2. Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP)
AHP is a mathematical technique used for multi-criteria decision-making. In a way it is better than other multicriteria techniques, as it is designed to incorporate tangible as well as non-tangible factors especially where the subjective judgments of different individuals constitute an important part of decision making [4]. Apart from other facts, this is rooted in the special structure of the AHP, which follows the intuitive way in which managers solve problems, and in its easy handling compared with other multi criteria decision-making procedures. Hence the intuitively solved decision problems can now be solved as procedure-orientated using AHP. The use of AHP leads to both, more transparency of the quality of management decisions and an increase in the importance of AHP [5].
Because of its intuitive appeal and flexibility, many corporations and governments routinely use AHP for making major policy decisions. Applications of AHP can be seen in a wide range of areas like merit salary recommendation system [6], environmental impact assessment [7], credit evaluation of the manufacturing firms [8], indoor environment assessment [9], selection of alternative transportation options [10], performance measurement system [11], TQM implementation [12], evaluation of highway transportation [13], determination of key capabilities of a firm [14] and for evaluation of an AHP software [15] itself.
AHP uses a five-step process to solve decision problems. They are
• Create a decision hierarchy by breaking down the problem into a hierarchy of decision elements.
• Collect input by a pair wise comparison of decision elements.
• Determine whether the input data satisfies a consistency test. If it does not, go back to Step 2 and redo the pair wise comparisons.
• Calculate the relative weights of the decision elements.
• Aggregate the relative weights to obtain scores and hence rankings for the decision alternatives.
One of the major reasons for the popularity of AHP is that the decision maker does not require advanced knowledge of either mathematics or decision analysis to perform first two steps. Last three steps are computational and can be performed manually or using software such as Expert Choice. However, the first two are the steps where the decision maker is very much involved in the model. On the basis of the decision maker’s understanding of the problem, the hierarchy can be designed and pair wise comparisons can be made of the decision elements. AHP uses redundant judgments for checking consistency, and this can exponentially increase the number of judgments to be drawn out from decision makers [5,16-20].
The AHP method can tolerate the inconsistency by providing the measurement of assessment inconsistency. This measurement is one of the important elements in priority determination process according to pairwise comparison. The higher consistency ratio, the assessment result becomes more inconsistent. The acceptable consistency ratio is less than or equal to 10 percent, although in some cases the consistency ratio which is higher than 10 percent is still considered acceptable [21].
According to Taylor III [15], Consistency Index (CI) can be calculated by using formula as follows:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
After acquiring Consistency Index (CI), the next step is calculating Consistency Ratio (CR) by using formula (3):
 (3)
(3)
Description:
N = Amount of items compared
wi = Weight
ci = Sum of column
CR = Consistency Ratio
CI = Consistency Index
RI = Random Consistency Index
Random Consistency Index (RI) can be observed in Table 1 as follows:
If CR ≥ 10%, the data acquired is inconsistent
If CR < 10%, the data acquired is consistent
The test of consistency result will be very useful in the AHP method. If the test result is inconsistent (CR ≥ 10%).
Then the result from the AHP method will be of no use in decision making.
Figure 2 illustrates the steps needed to be taken in this research for AHP method.
3. Fuzzy Expert Systems
The world of information is surrounded by uncertainty and imprecision. The human reasoning process can handle inexact, uncertain, and vague concepts in an appropriate manner. Usually, the human thinking, reasoning, and perception process cannot be expressed precisely. These types of experiences can rarely be expressed or measured using statistical or probability theory. Fuzzy logic provides a framework to model uncertainty, the human way of thinking, reasoning, and the perception process. Fuzzy systems were first introduced by Zadeh [22].
A fuzzy expert system is simply an expert system that

Figure 2. Steps needed to be taken in this research for AHP method.
uses a collection of fuzzy membership functions and rules, instead of Boolean logic, to reason about data [23].
Neuro-fuzzy modeling is concerned with the extraction of models from numerical data representing the behaviour of a system. The models in this case are rulebased and use the formalism of fuzzy logic, i.e. they consists of sets of fuzzy “if-then” rules with possibly several premises. The learning capability of feedforward neural networks supports the model extraction if the architecture of the network, once properly trained, may be translated into rules without loss of information. This idea has been thoroughly studied by several authors starting with the beginning of the nineties (see e.g. [24- 31]) and continues to be an important research area [32].
Figure 3 illustrates the basic architecture of a fuzzy expert system. The main components are a fuzzification interface, a fuzzy rule base (knowledge base), an inference engine (decision-making logic), and a defuzzifi- cation interface. The input variables are fuzzified whereby the membership functions defined on the input variables are applied to their actual values, to determine the degree of truth for each rule antecedent. Fuzzy if-then rules and fuzzy reasoning are the backbone of fuzzy expert systems, which are the most important modeling tools based on fuzzy set theory. The fuzzy rule base is characterized in the form of if-then rules in which the antecedents and consequents involve linguis-tic variables. The collection of these fuzzy rules forms the rule base for the fuzzy logic system. Using suitable inference procedure, the truth value for the antecedent of each rule is computed, and applied to the consequent part of each rule. This results in one fuzzy subset to be assigned to each output variable for each rule. Again, by using suitable composition procedure, all the fuzzy subsets assigned to each output variable are combined together to form a single fuzzy subset for each output variable. Finally, defuzzification is applied to convert the fuzzy output set to a crisp output. The basic fuzzy inference system can take either fuzzy inputs or crisp inputs, but the outputs it produces are always fuzzy sets. The defuzzification task extracts the crisp output that best represents the fuzzy set. With crisp inputs and outputs, a fuzzy inference system implements a nonlinear mapping from its input space to output space through a number of fuzzy if-then rules.
In what follows, the two most popular fuzzy inference systems are introduced that have been widely deployed in various applications. The differences between these two fuzzy inference systems lie in the consequents of their fuzzy rules, and thus their aggregation and defuzzification procedures differ accordingly.
According to Mamdani, fuzzy inference system [33]— see Figure 4—the rule ante-cedents and consequents are defined by fuzzy sets and has the following structure:

Figure 3. Basic architecture of a fuzzy expert system.

Figure 4. Mamdani fuzzy inference system using min and max for T-norm and T-conorm operators.
if x is A1 and y is B1 then z1 =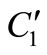 .
.
There are several defuzzification techniques. The most widely used defuzzification technique uses the centroid of area method as follows:
 (4)
(4)
where µA(z) is the aggregated output MF.
Also a neuro-fuzzy model comes from combining fuzzy logic with neural networks to give a system of postulates, data and inferences to describe an object or process. Some of the ways of combining fuzzy logic and neural networks to create a neuro-fuzzy model are: 1) to use a supervised learning technique to build a rule based fuzzy model; 2) to use a non supervised learning technique to build a rule based fuzzy model; 3) to use a non supervised learning technique to make a partition of the input space. One of the most popular and well documented neuro-fuzzy systems is ANFIS, which has a good software support [34]. Jang [35] present the ANFIS architecture and application examples in modeling a nonlinear function, a dynamic system identification and a chaotic time series prediction. Given its potential in building fuzzy models with good prediction capabilities, the ANFIS architecture was chosen for modeling in this work.
Figure 5 shows the block diagram of ANFIS structure.
Our model is based on the Adaptive Network Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) and Mamdani, fuzzy inference system.
4. Framework of Research
The proposed model has been established based on this principle that each real level of transactions in B2C websites includes 3 major factors and 12 sub factors as figure 6 after prioritization using AHP.
Table 2 shows 12 sub factors of research model.