The low-temperature (
T = 2 K) exciton-polariton luminescence (EPL) spectra in the vicinity of the exciton-resonance frequency
An=1 for CdS-type crystals have been theoretically and experimentally investigated with allowance for the mechanical exciton decay
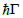
. The results of the numerical calculations of the partial and interference contributions of the bulk and radiative surface spectral modes to the EPL in the geometry of additional s- and p-polarized waves emitted into vacuum are analyzed. It is shown that the contributions of purely longitudinal excitons and their interference with polaritons of the upper dispersion branch near the longitudinal frequency
ωL to the EPL are small (
∼10% - 30%); nevertheless, they must be taken into account to obtain quantitative agreement with experimental data. Specifically these contributions are responsible for the formation of an additional
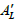
line (along with the fundamental
AT line) in the case of oblique incidence of radiation.