We proceed to obtain a polynomial based iterative solution for early universe creation of the Higgs boson mass, using a derived polynomial of the form
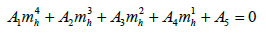
with the coefficients for
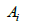
derived through a series of specific integral formulations with
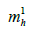
the mass of a Higgs boson, and the construction of the coefficients derived as of
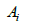
the using a potential system, for the Higgs, largely similar to the usual Peskin and Schroeder quantum field theoretic treatment for a Higgs potential, which subsequently is modified, i.e. this is for the regime of space-time as up to the Electro-weak regime of cosmology, in terms of a spatial regime. The linkage to Dark matter is in terms of the Scalar Singlet Dark matter model proposed by Silvera and Zee, i.e. what we do is to use a procedure similar to the usual Standard model Higgs, but to find ways to iterate to isolate key inputs into electro weak symmetry breaking procedure for the creation of Dark Matter. Afterwards, we will use specific inputs into the Scalar Singlet Dark matter model which would isolate out input parameters which we think are amendable to experimental testing. We conclude with a discussion of entropy so generated, along the lines of a modification of the usual branching ratios used in Higgs physics, with spin offs we think are relevant to the Dark Matter problem. We also use it to critique some linkage between Dark Matter, and gravity, which may explain some of the findings of LIGO, which were reviewed in 2016 in one of our listed references.